What is desktop management and how does it work?
Desktop management is a comprehensive approach to managing all the computers within an organization. Despite its name, desktop management can include overseeing, monitoring and upgrading laptops, smartphones and IoT computing devices, as well as desktop computers.
Desktop management is a component of systems management, which is the administration of all components of an organization's IT systems.
How does desktop management work?
Traditional desktop management tasks include installing and maintaining hardware and software, using spam filtering and administering user permissions.
However, security-related tasks have become an increasingly large part of desktop management for IT departments in recent years. As a result, an ever-larger proportion of administrative resources has shifted to security-related tasks, including the following:
- using patch management;
- implementing IT asset management;
- installing antivirus and antispyware software;
- regulating shadow IT applications -- i.e., programs installed without corporate approval;
- provisioning and auditing devices; and
- supporting remote access for off-site team members or troubleshooting via off-site security management or help desk personnel.
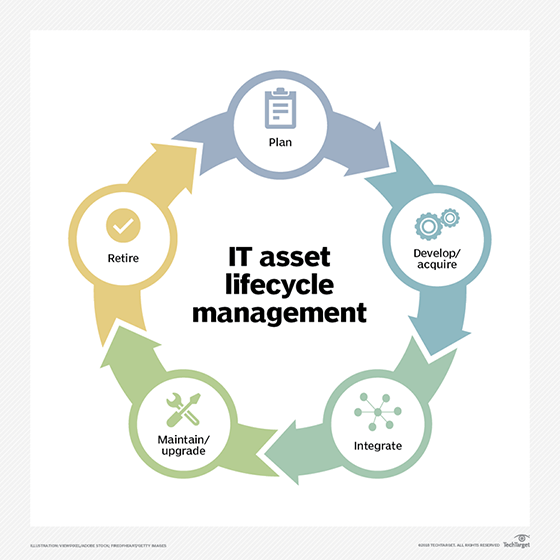
What is Desktop Management Interface?
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) was a framework to centrally manage and track hardware and software elements in a system of PCs. It officially reached its end-of-life status on March 31, 2005, when it was replaced by a collection of DMTF standards known as Desktop and Mobile Architecture for System Hardware (DASH).
DASH relies heavily on the Common Information Model (CIM), which helps system administrators control devices and applications from multiple manufacturers. Using CIM and the WS-Management specification, DASH facilitates collecting, monitoring and managing several desktop and mobile systems.
Why is desktop management important?
When properly implemented, desktop management tools can boost efficiency and productivity, improve security and help IT administrators support endpoint devices through their lifecycle.
Organizations can use desktop management and unified endpoint management (UEM) to ensure that users apply security best practices, patches are pushed out and installed regularly, and only authorized users and devices are permitted access to the network.
What is remote desktop management?
As remote work grows increasingly prevalent, organizations must adopt tools and processes that allow work and tech support to remain seamless.
A remote desktop enables a user to connect to a computer in another location and interact with it as if they were accessing it locally. Remote desktop management also allows IT to oversee a user's local desktop, regardless of its location, and ensure that patches are correctly installed, only authorized devices connect to the network, and any system or software errors are identified and solved with minimal disruption to work. A remote desktop connection is made possible with one of several protocols, including Microsoft's remote desktop protocol, virtual network computing or others.
Desktop management tools
Managing endpoint devices has necessitated the use of multiple specialized tools. Over time, these tools have consolidated into UEM. Whether presented as individual offerings or aspects of a UEM platform, these tools include the following:
- Application portfolio management and application lifecycle management. APM and ALM govern the allowed and denied lists of apps available for use by employees on their work devices.
- Mobile device management. MDM concentrates on managing the lifecycle of end-user devices, whether provisioned by the organization or supplied by the employee.
- Mobile application management. MAM oversees enterprise applications on corporate and personal smartphones and tablets.
- Remote desktop management software. This software focuses on remote users and their devices. Functions include maintaining and auditing remote technology, and ensuring that proper antivirus and VPN programming are installed.
- Identity and access management. IAM monitors access permissions for authorized users, applications, devices and data. IAM also supports authentication protocols, such as single sign-on (SSO), two-factor authentication (2FA) and certificate management.
How to choose desktop management software
Choosing the right desktop management software has become increasingly complex as the number of an organization's mobile devices, desktops and software components grows. The rise of UEM aims to simplify this process by creating a centralized platform.
When comparing desktop management and UEM tools, the determining factor will often be how a particular offering handles certain features, such as patch management, remote access, asset management and tracking, content management, security and more.
While Windows continues to be the dominant OS in many organizations, macOS is becoming increasingly popular, and IT must find the right endpoint management tool to support it. These platforms are either specially tailored for macOS -- and other Apple devices -- or have tools that can support multiple OSes. Choosing the best macOS management software is dependent on the organization's endpoint and user requirements, budget and a close examination of the offered features.
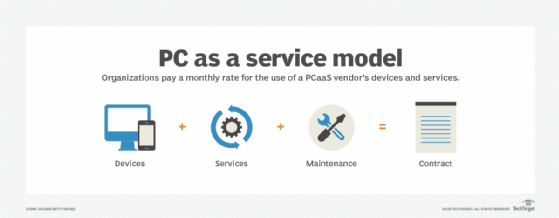
As organizations consider what OSes they plan to support, many vendors are beginning to offer alternative models for endpoint procurement and management. Device as a service and PC as a service are device lifecycle management models that outsource hardware and management services to the vendor in exchange for a lease or monthly subscription.
These as-a-service models ease the strain on IT and can be especially beneficial for smaller organizations or those with a strict budget. It's important to note that these are different from desktop as a service, a cloud computing offering for virtual desktops.
What are the benefits of desktop management?
There are several benefits associated with implementing a desktop management initiative within an organization, including the following:
- improved security through capabilities such as SSO, 2FA, encryption and more;
- increased IT productivity through automation of management system processes;
- enhanced collaboration capabilities, as dispersed teams can connect and communicate through cloud-based tools in real time;
- permission controls that help eliminate unnecessary access by team members to sensitive data and systems; and
- cost savings through the automation of repetitive, rules-based desktop management tasks.
What are the challenges of desktop management?
The IT department faces several challenges, including those listed below, as they focus on desktop and endpoint management across an organization:
- implementing simultaneous software upgrades and security patches across the organization on every endpoint device;
- reducing operational costs associated with lifecycle management, patch management and troubleshooting systems; and
- managing hardware and software from multiple vendors to ensure they meet all compliance and security needs.