Network File System (NFS)
What is NFS?
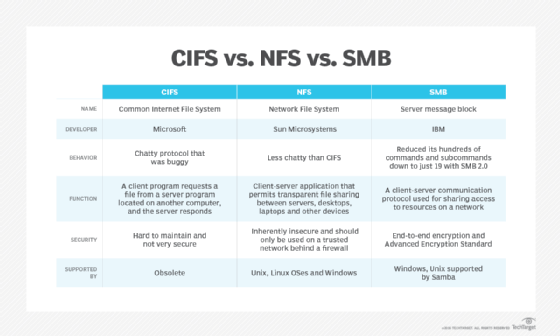
Network File System (NFS) is a networking protocol for distributed file sharing. A file system defines the way data in the form of files is stored and retrieved from storage devices, such as hard disk drives, solid-state drives and tape drives. NFS is a network file sharing protocol that defines the way files are stored and retrieved from storage devices across networks.
The NFS protocol defines a network file system, originally developed for local file sharing among Unix systems and released by Sun Microsystems in 1984. The NFS protocol specification was first published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an internet protocol in RFC 1094 in 1989. The current version of the NFS protocol is documented in RFC 7530, which documents the NFS version 4 (NFSv4) Protocol.
NFS enables system administrators to share all or a portion of a file system on a networked server to make it accessible to remote computer users. Clients with Authorization to access the shared file system can mount NFS shares, also known as shared file systems. NFS uses Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) to route requests between clients and servers.
NFS is one of the most widely used protocols for file servers. NFS implementations are available for most modern operating systems (OSes), including the following:
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise HP-UX
- IBM AIX
- Microsoft Windows
- Linux
- Oracle Solaris
Cloud vendors also implement the NFS protocol for cloud storage, including Amazon Elastic File System, NFS file shares in Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Filestore.
Any device that can be attached to an NFS host file system can be shared through NFS. This includes hard disks, solid state drives, tape drives, printers and other peripherals. Users with appropriate permissions can access resources from their client machines as if those resources are mounted locally.
NFS is an application layer protocol, meaning that it can operate over any transport or network protocol stack. However, in most cases NFS is implemented on systems running the TCP/IP protocol suite. The original intention for NFS was to create a simple and stateless protocol for distributed file system sharing.
Early versions of NFS used the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for its transport layer. This eliminated the need to define a stateful storage protocol; however, NFS now supports both the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and UDP. Support for TCP as a transport layer protocol was added to NFS version 3 (NFSv3) in 1995.
How does the Network File System work?
NFS is a client-server protocol. An NFS server is a host that meets the following requirements:
- has NFS server software installed;
- has at least one network connection for sharing NFS resources; and
- is configured to accept and respond to NFS requests over the network connection.
An NFS client is a host that meets the following requirements:
- has NFS client software installed;
- has network connectivity to an NFS server;
- is authorized to access resources on the NFS server; and
- is configured to send and receive NFS requests over the network connection.
NFS was initially conceived as a method for sharing file systems across workgroups using Unix. It is still often used for ad hoc sharing of resources.
The process of setting up NFS service includes the following three steps, whether on an enterprise file server or on a local workstation:
- Verify that rpc.mountd or just mountd is installed and working. This is the NFS daemon -- the program that listens to the network for NFS requests.
- Create or choose a shared directory on the server. This is the NFS mount point. Using the mount point and the server host name or address uniquely identifies the NFS resource.
- Configure permissions on the NFS server to enable authorized users to read, write and execute files in the file system.
Setting up an NFS client machine to access an NFS server can be done manually, using the mount command or using an NFS configuration file -- /etc/exports. Each line in the NFS config file contains a mount point, an IP address or a host domain name and any configuration metadata needed to access the file system.
Versions of NFS
NFSv4, the current version of NFS, and other versions subsequent to NFS version 2 (NFSv2) are usually compatible after client and server machines negotiate a connection.
NFS versions from the earliest to the current one are as follows:
Sun Network Filesystem released March 1984
Sun Microsystems published the first implementation of its network file system in March 1984. The objective was to provide transparent, remote access to file systems. Sun intended to differentiate its NFS project from other Unix file systems by designing it to be easily portable to other OSes and machine architectures.
NFSv2 released March 1989
NFSv2 is specified in RFC 1094. Its key features included the following:
- It uses UDP as its transport protocol. This enables keeping the server stateless, with file locking implemented outside of the core protocol.
- Its file offsets are limited to 32-bit quantity, making the maximum size of files clients can access 4.2 GB.
- Its data transfer size is limited to 8 KB, and it requires that NFS servers commit data written by a client to a disk or non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) before responding.
NFSv2 is obsolete and should not be used.
NFSv3 released June 1995
Specified in RFC 1813, NFSv3 incorporated the following new features and updates:
- It extended file offsets from 32- to 64-bits, which removed the 4.2 GB maximum file size limit.
- It relaxed the 8 KB data transfer limitation rule to enable larger read and write transfers.
- TCP was added as a transport layer protocol option in NFSv3. TCP transport makes it easier to use NFS over a wide area network (WAN) and enhances read and write transfer capabilities.
- Added a COMMIT operation enabling reliable asynchronous writes, and an ACCESS RPC that improves support for access control lists, or ACLs, and Power users.
- The server replies to WRITE RPCs instantly in NFSv3, without syncing to a disk or NVRAM. To ensure data is on stable storage, the client only needs to send a COMMIT RPC.
NFSv3 is reported to still be in widespread use. It is interoperable with NFSv4 but lacks support for many of the new and improved features rolled out with later versions.
NFSv4 released April 2003
The update to NFSv4 was first documented in RFC 3010 in 2000. This is the first version of the NFS specification that the IETF published as a proposed standard; prior versions were published as informational.
New and improved features in this update included the following:
- support for strong authentication, integrity and privacy;
- support for advanced file caching;
- improved internationalization capability;
- better interoperability with Microsoft Windows filesharing was added;
- better support for integrated locking was added; and
- improved performance and reliability because communication was handled with compound RPCs and TCP use was required.
A new API was included for future additions of new security mechanisms.
A slightly-updated version of the NFS specification was republished in 2003 as RFC 3530, to correct errors in the first version and add some improvements to the protocol.
NFS version 4.1 (NFSv4.1) released January 2010
A minor version protocol, NFSv4.1 published as RFC 5661, added new features including the following:
- It enabled the use of NFS on global WANs.
- It standardized parallel NFS to address bandwidth and scalability issues.
- It internationalized support using UTF-8 encoding for file names, directories and other identifiers. UTF-8 replaces the ASCII character set. It is a variable width character encoding that is as compact as ASCII but can also contain Unicode
- It added a new session model to maintain the server's state relative to the connections belonging to the client.
- Directory delegation added the ability to delegate file operations to the accessing client.
NFS version 4.2 (NFSv4.2) released November 2016
NFSv4.2 is documented in RFC 7862. It added the following new features and updates:
- enhanced modern scale-out storage architectures;
- support for server-side copy, which enables cloning and snapshots of files by any NFSv4.2 storage server;
- space reservations to ensure a file will have storage available;
- support for sparse files, which contain large blocks of zero data that are transferred as zeros when read from the file;
- support for application data block support, which defines the format of a file;
- support for labeled NFS, which supports additional security when used with Security-Enhanced Linux.
Benefits of NFS
Among many benefits for organizations using NFS are the following:
- Mature. NFS is a mature protocol, which means most aspects of implementing, securing and using it are well understood, as are its potential weaknesses.
- Open. NFS is an open protocol, with its continued development documented in internet specifications as a free and open network protocol.
- Cost-effective. NFS is a low-cost solution for network file sharing that is easy to set up because it uses the existing network infrastructure.
- Centrally managed. NFS's centralized management decreases the need for added software and disk space on individual user systems.
- User-friendly. The protocol is easy to use and enables users to access remote files on remote hosts in the same way they access local ones.
- Distributed. NFS can be used as a distributed file system, reducing the need for removable media storage devices.
- Secure. With NFS, there is less removeable media like CDs, DVDs, Blu-ray disks, diskettes and USB drives in circulation, making the system more secure.
Disadvantages of NFS
Some of the drawbacks of using NFS include the following:
- Dependence on RPCs makes NFS inherently insecure and should only be used on a trusted network behind a firewall. Otherwise, NFS will be vulnerable to internet threats.
- Some reviews of NFSv4 and NFSv4.1 suggest that these versions have limited bandwidth and scalability and that NFS slows down during heavy network traffic. The bandwidth and scalability issue is reported to have improved with NFSv4.2.
While NFS started out as a simple network file system for local area networking, it has been adapted and adopted for almost every kind of distributed file system. Find out how AWS implements its file services -- Amazon FSx and Amazon EFS -- based on Windows Server Message Block and NFS.








