Windows Defender Application Guard
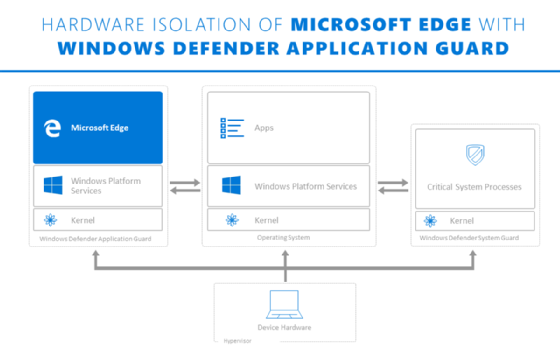
Windows Defender Application Guard is a security tool built into Microsoft Edge that isolates browser sessions from the desktop in a virtual machine (VM) to prevent any malicious activity from reaching the desktop.
Windows Defender Application Guard is part of the Windows Defender security program that comes built in to Windows 10. Microsoft first added Microsoft Windows Defender to Windows Vista deployments in 2006. The company debuted Windows Defender Application Guard in the Fall Creators Update for Windows 10 in 2017.
IT professionals can set a whitelist of sites that do not need to run Windows Defender Application Guard, and all other sites that users access open through the security tool. When a user accesses a site through Windows Defender Application Guard, Edge runs the site through an isolated container stored in Microsoft Hyper-V Cloud.
Purpose
Windows Defender Application Guard runs isolated browser sessions to protect against several vulnerability types, including malware and zero-day attacks.
When Windows Defender Application Guard opens a site, the browser display changes so the user knows he is on a non-whitelisted site and his current browser session is isolated. Microsoft Edge is automatically set as the preferred browser in Windows 10, so IT must ensure that users maintain this setting through Group Policy to take advantage of Windows Defender Application Guard.
After each session ends, the container deletes all of its history and is immediately ready to run a new session. The session doesn't store any cookies from the session and prevents the browser from accessing local storage.
Windows Defender Application Guard has two settings for administration: stand-alone and enterprise-managed modes. Stand-alone mode allows the desktop user to manage his settings on his own. Enterprise-managed mode allows IT professionals to control the tool.
What it protects
IT professionals can use Windows Defender Application Guard for various device use cases. PCs and laptops are the simplest to manage and protect because IT can guarantee these devices typically run their connection through the corporate network. This allows IT to manage the endpoints with Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager.
For BYOD laptops, IT has less control over the devices. If users work remotely, the devices won't always connect to the internet through the corporate network. Generally, users retain administrator privileges for the devices they own, so IT must use Microsoft Intune, Group Policy or a similar tool to manage these devices.
Microsoft designed Windows Defender Application Guard for Microsoft Edge, but Internet Explorer also supports the tool if an organization uses that browser to support legacy applications or because its users prefer Internet Explorer.








